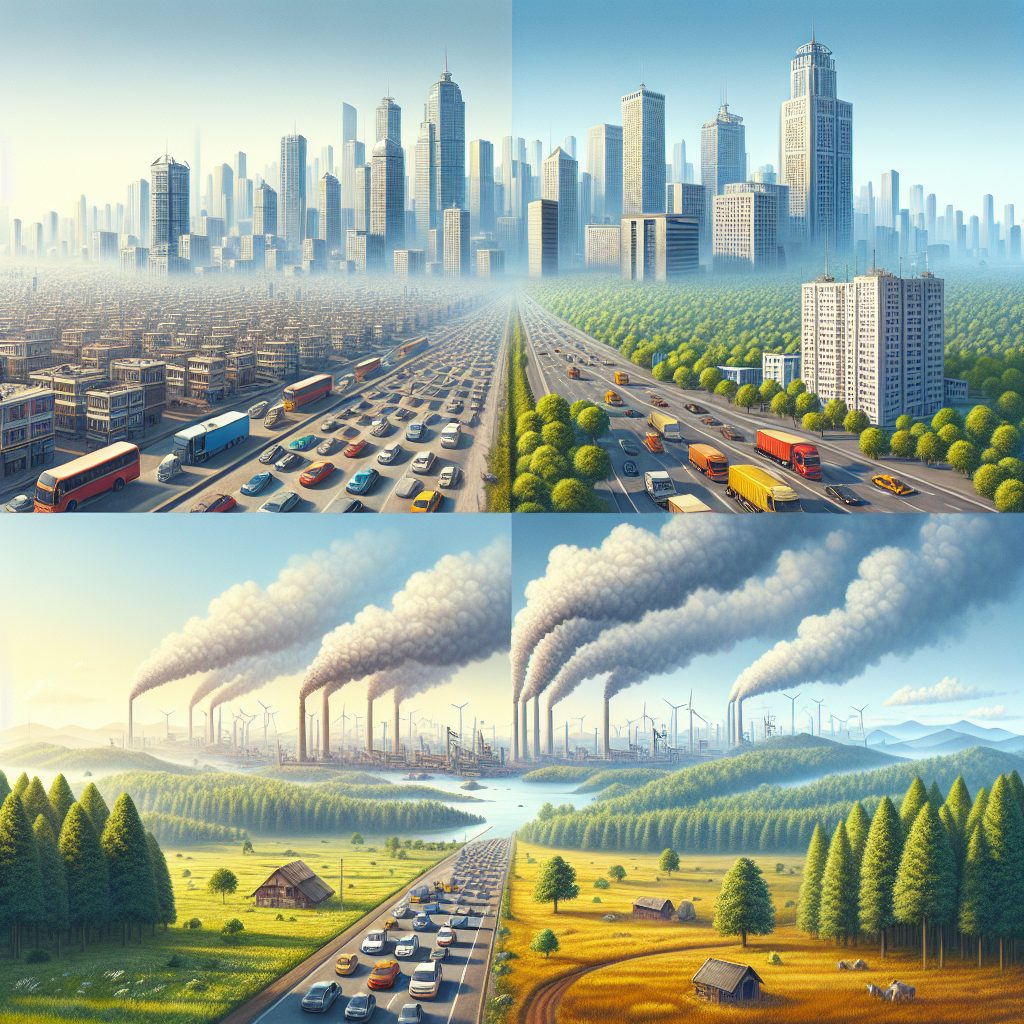
Air quality is a crucial factor that impacts the health and well-being of individuals and communities alike. It refers to the level of pollutants and contaminants present in the air we breathe. When comparing air quality in urban and rural areas, it becomes evident that there are notable differences between the two environments.
In urban areas, the presence of various industries, transportation systems, and high population density significantly contributes to the deterioration of air quality. These sources release pollutants such as particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and volatile organic compounds, which can lead to respiratory issues, cardiovascular diseases, and other health complications. On the other hand, rural areas generally have fewer pollution sources, and their air quality is often considered better due to less human activity and industrialization. However, it’s important to note that agricultural practices, including the use of pesticides and fertilizers, can also contribute to air pollution in some rural areas.
In the upcoming sections, we will delve deeper into the impacts of air quality on human health in both urban and rural settings. Furthermore, we will explore the unique features of air pollution in each environment, providing valuable insights into the factors that contribute to these differences. By examining these key takeaways, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of the complexities surrounding air quality and its repercussions in urban and rural areas.
key Takeaways
1. Urban areas have higher pollution levels than rural areas due to factors such as industrial activities, high population density, and heavy traffic.
2. The presence of air pollutants in urban areas can lead to adverse health effects, including respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
3. Despite efforts to improve air quality, urban areas continue to face challenges such as vehicle emissions, construction activities, and limited green spaces.
4. Rural areas generally have better air quality due to lower levels of pollution sources and the presence of more natural and open spaces.
5. It is crucial to implement effective strategies and policies to mitigate air pollution in urban areas, such as promoting renewable energy, enhancing public transportation, and implementing stricter emission regulations.
Is Air Quality Better in Urban or Rural Areas?
Understanding the Factors Affecting Air Quality
Air quality is an essential aspect of our daily lives, as it directly impacts our health and overall well-being. When comparing air quality between urban and rural areas, several factors come into play.
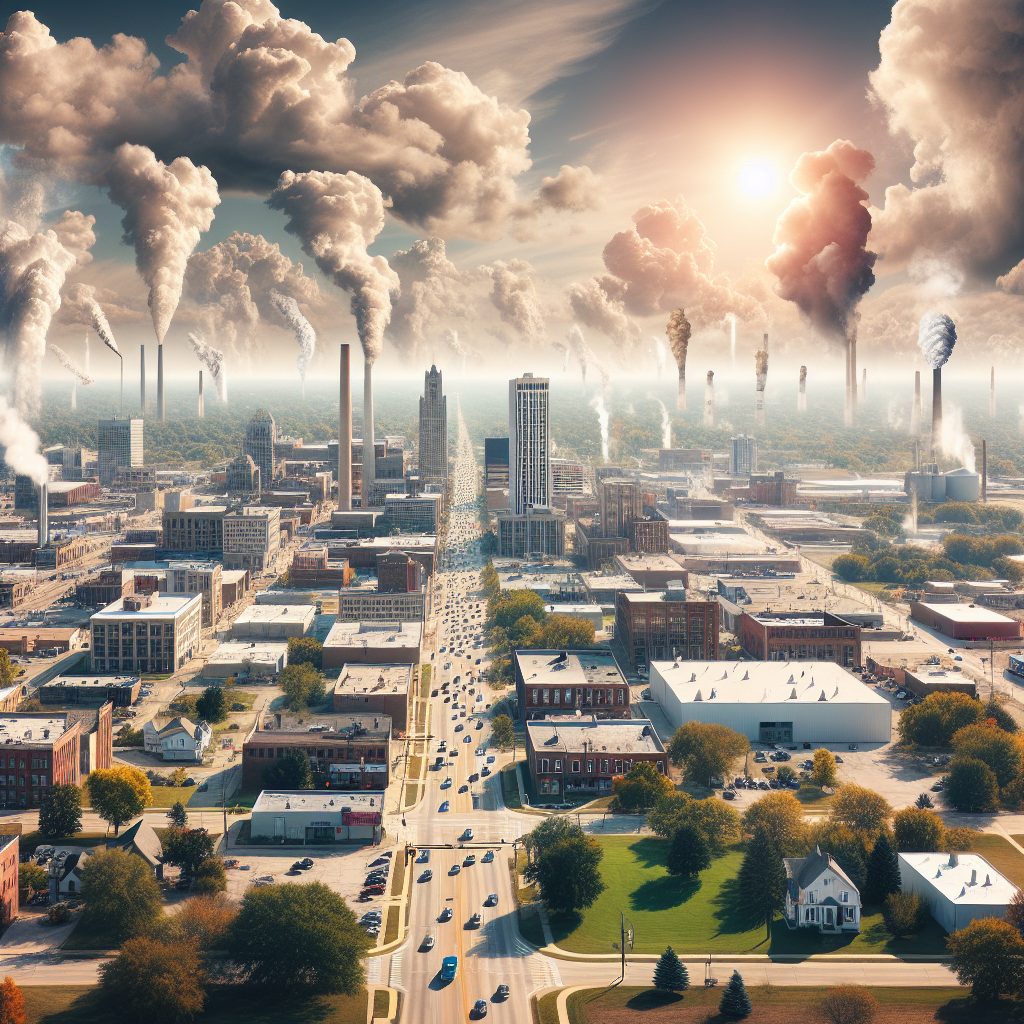
One of the main factors influencing air quality in urban areas is the high concentration of human activities. Industries, transportation systems, and residential areas all contribute to the release of pollutants, such as greenhouse gases, particulate matter, and carbon monoxide. These emissions can lead to increased air pollution, reducing the quality of the air we breathe.
On the other hand, rural areas typically have fewer human activities and lower population densities. As a result, the release of pollutants is generally lower compared to urban areas. This can contribute to better air quality in rural regions.
The Impact of Traffic on Air Quality
Traffic is a significant contributor to air pollution, particularly in urban areas. The high volume of vehicles, coupled with traffic congestion, results in increased emissions of pollutants like nitrogen oxides and fine particles. These emissions have detrimental effects on air quality, leading to smog formation and health issues.
Rural areas, with fewer vehicles on the roads, experience lower levels of traffic-related air pollution. However, it’s essential to consider that some rural areas may have roadways that serve as significant transportation routes, which can also lead to increased pollutant emissions.
The Role of Industrial Activities
Industrial activities play a crucial role in air quality in both urban and rural areas. Urban regions often host a variety of industries, including manufacturing, power generation, and construction, which emit pollutants directly into the air. These emissions can have severe consequences on air quality, leading to smog, acid rain, and the deterioration of public health.
Rural areas may also have industrial activities, albeit on a smaller scale. Farms, for example, can contribute to air pollution through the release of agricultural emissions, including ammonia and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These emissions can have localized effects on air quality, particularly in areas with intensive farming practices.
Natural Factors and Air Quality
Beyond human activities, natural factors also influence air quality in both urban and rural areas. Weather conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and wind patterns, play a vital role in dispersing pollutants and affecting air quality levels. Urban areas often experience the “urban heat island effect,” where higher temperatures intensify the reactions of pollutants, reducing air quality even further.
Rural areas, with their abundance of vegetation and open spaces, can have better air quality due to natural air purification processes. Trees and plants help absorb pollutants and release oxygen through photosynthesis, leading to cleaner air. However, certain natural factors, such as wildfires or agricultural burning, can temporarily deteriorate air quality in rural regions.
Conclusion
When examining the air quality in urban and rural areas, it becomes evident that multiple factors contribute to the differences observed. While urban areas tend to have higher levels of air pollution due to human activities and traffic, rural areas benefit from lower population densities and reduced industrialization. However, natural factors and localized emissions from farming practices can still impact air quality in rural regions. It is crucial to address these factors collectively to improve air quality and protect public health.
Top 5 Tips for Improving Air Quality
- Reduce vehicle emissions by using public transportation, carpooling, or opting for electric vehicles.
- Support green initiatives and policies aimed at reducing pollution from industrial activities in urban areas.
- Promote sustainable farming practices in rural areas to minimize pollutant emissions from agricultural activities.
- Plant trees and vegetation to increase natural air purification processes in both urban and rural areas.
- Stay informed about air quality levels in your area and take necessary precautions, such as wearing masks during periods of poor air quality.
Air Quality in Urban vs. Rural Areas
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What factors contribute to air pollution in urban areas?
Urban areas can experience high levels of air pollution due to factors such as vehicular emissions, industrial activities, construction sites, and dense population.
2. How does air quality in rural areas differ from urban areas?
Rural areas generally have cleaner air compared to urban areas as they are less affected by industrial pollution, traffic congestion, and other urban sources. However, rural regions might still face air pollution issues from agricultural activities or natural factors like dust or wildfire smoke.
3. Is it true that urban areas have higher levels of particulate matter (PM) pollution?
Yes, urban areas tend to have higher levels of particulate matter pollution, especially PM2.5, which consists of fine particles that can penetrate deep into the lungs and pose health risks. The sources of PM pollution in urban areas include vehicle exhaust, industrial emissions, and combustion processes.
4. Are there any health risks associated with living in urban areas with poor air quality?
Living in urban areas with poor air quality can increase the risk of respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, exacerbate existing respiratory conditions, and have adverse effects on overall health. Long-term exposure to air pollution in cities can lead to chronic health issues.
5. Can air quality in rural areas be affected by agricultural practices?
Yes, agricultural activities such as crop burning, use of pesticides, and livestock emissions can contribute to air pollution in rural areas. These practices can release pollutants like ammonia, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and agricultural dust, impacting the local air quality.
6. How can individuals protect themselves from poor air quality in urban areas?
Individuals can protect themselves by staying updated on air quality index reports, limiting outdoor activities during high pollution days, using air purifiers indoors, wearing masks when necessary, and promoting sustainable transportation options to reduce vehicle emissions.
7. Do rural areas have any advantages in terms of air quality?
Yes, rural areas often offer advantages in terms of air quality due to fewer sources of pollution. The presence of more natural spaces, greenery, and lower population density in rural areas can contribute to cleaner and fresher air.
8. How can governments improve air quality in urban regions?
Governments can improve air quality in urban regions through measures like promoting cleaner technologies, enforcing stricter emission standards for industries and vehicles, investing in public transportation systems, implementing green energy initiatives, and raising awareness about the importance of reducing air pollution.
9. Can air pollution from urban areas affect neighboring rural regions?
Yes, air pollution from urban areas can spread to neighboring rural regions depending on factors such as wind patterns, geographical features, and proximity. Pollutants can be carried over long distances, affecting the air quality in rural areas surrounding urban centers.
10. Are there any initiatives in place to monitor and control air pollution in both urban and rural areas?
Yes, many initiatives exist to monitor and control air pollution in both urban and rural areas. These include air quality monitoring networks, emission reduction programs, public awareness campaigns, and collaborations between environmental agencies, communities, and industries to combat air pollution.
Final Thoughts:
The disparities in air quality between urban and rural areas are significant, with urban regions generally experiencing higher pollution levels due to increased anthropogenic activities. However, it is crucial to acknowledge that rural areas are not immune to air pollution, as they can face their own unique challenges.
Efforts must be made by governments, communities, and individuals alike to address air pollution and strive for healthier environments. By adopting sustainable practices, reducing emissions, and implementing effective policies, we can ensure better air quality not only in urban areas but also in rural areas, enhancing the overall well-being of both populations.